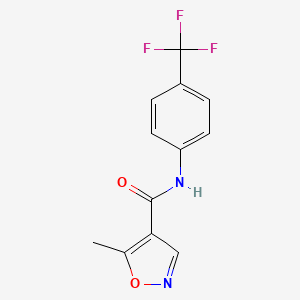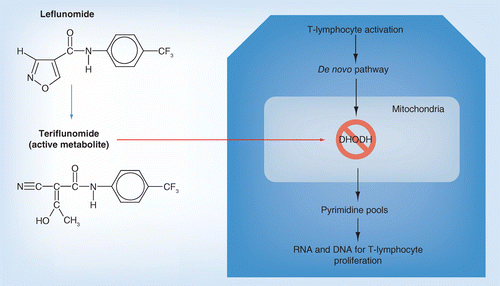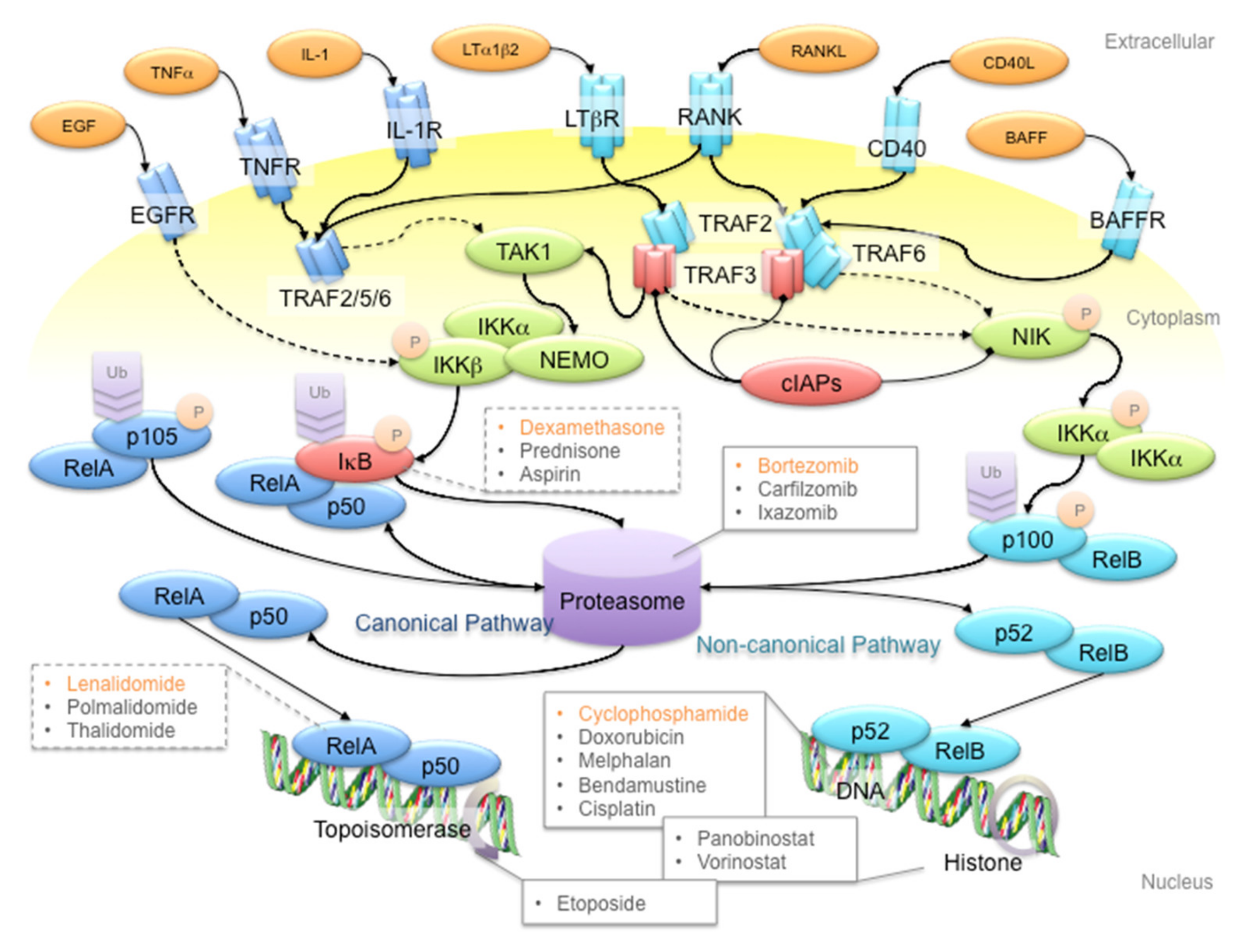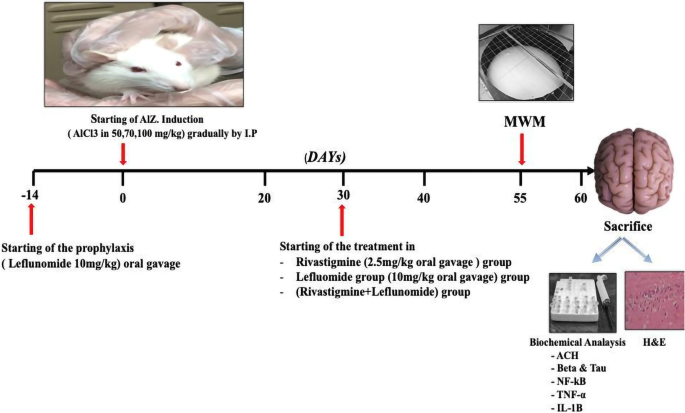
Leflunomide abrogates neuroinflammatory changes in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease: the role of TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β axis inhibition | SpringerLink

The active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, interferes with dendritic cell function | Arthritis Research & Therapy | Full Text

NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation | American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology

Leflunomide an immunomodulator with antineoplastic and antiviral potentials but drug-induced liver injury: A comprehensive review - ScienceDirect

Leflunomide an immunomodulator with antineoplastic and antiviral potentials but drug-induced liver injury: A comprehensive review - ScienceDirect

Leflunomide–hydroxychloroquine combination therapy in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (RepurpSS-I): a placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomised clinical trial - The Lancet Rheumatology
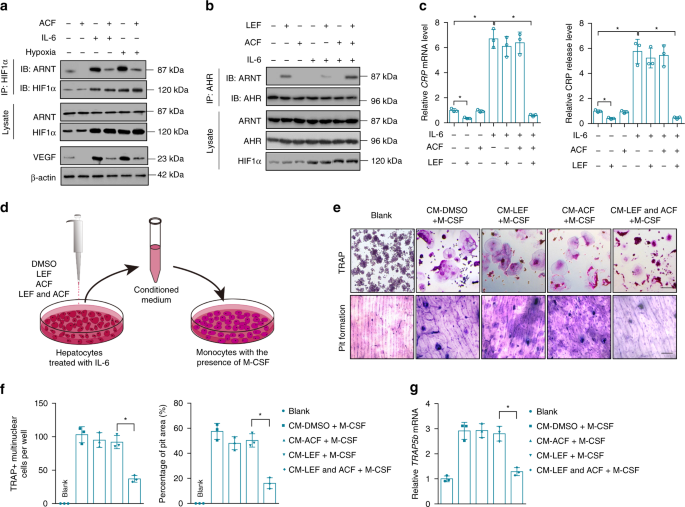
HIF1α inhibition facilitates Leflunomide-AHR-CRP signaling to attenuate bone erosion in CRP-aberrant rheumatoid arthritis | Nature Communications